Archives
- 2026-03
- 2026-02
- 2026-01
- 2025-12
- 2025-11
- 2025-10
- 2025-09
- 2025-03
- 2025-02
- 2025-01
- 2024-12
- 2024-11
- 2024-10
- 2024-09
- 2024-08
- 2024-07
- 2024-06
- 2024-05
- 2024-04
- 2024-03
- 2024-02
- 2024-01
- 2023-12
- 2023-11
- 2023-10
- 2023-09
- 2023-08
- 2023-07
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2019-06
- 2019-05
- 2019-04
- 2018-07
-
Our previous studies found that some steroid
2025-01-21
Our previous studies found that some steroid mimetic structures such as stilbene, biphenyl, naphthalene and benzothiophene rings were suitable for lipophilic moieties of 17,20-lyase inhibitors, and several inhibitors obtained using a steroid A, C-ring mimetic approach have already been published. Du
-
br Autophagy inducers Macroautophagy is often seen as a cell
2025-01-21
Autophagy inducers Macroautophagy is often seen as a cellular process capable of increasing the fitness of Praziquantel and overcome resistance to several forms of stress [9], [10]. As discussed above, it has been proposed by several authors that an effective strategy for enhancing sensitivity of
-
br Autophagy inducers Macroautophagy is often seen as a cell
2025-01-21
Autophagy inducers Macroautophagy is often seen as a cellular process capable of increasing the fitness of PND-1186 FAK inhibitor and overcome resistance to several forms of stress [9], [10]. As discussed above, it has been proposed by several authors that an effective strategy for enhancing sens
-
br Introduction The process of
2025-01-21
Introduction The process of mitosis is highly complex and tightly regulated. This phase of the Quetiapine resulted in two identical daughter cells. The aurora kinases (aurora A, B, and C) are a family of three highly homologous serine-threonine protein kinases that play a key role in regulating
-
In HepG cells compound showed
2025-01-21
In HepG2 cells, Reparixin showed inhibition of total lipid syntheses with an IC of 8μM. A cell based Alamar Blue cytotoxicity assay was used in parallel to differentiate the effect on the inhibition of lipid synthesis versus potential cytotoxicity. Under identical incubation conditions, compound sho
-
br Acknowledgements M M M
2025-01-20
Acknowledgements M.M.M. is the William Dow Lovett Professor of Neurology and is supported by grants from the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson's Research, the American Parkinson Disease Association, the New Jersey Health Foundation/Nicholson Foundation, and by the National Institutes of Hea
-
Furthermore we also found that the basic level of ROS
2025-01-20
Furthermore, we also found that the basic level of ROS was markedly lower in mtDNA-reduced SW480 gamma secretase inhibitors than that in the parent cells. Endogenous ROS is most notably produced at the sites of complex I and complex III [5], it might be plausible that the decreased quantity of ROS
-
Over the years measures of total
2025-01-20

Over the years, measures of total antioxidant status (TAS) have been developed to capture the collective effect of antioxidant defense capacity, including enzymatic and nonenzymatic systems (Fraga et al., 2014, Franco et al., 2007). Multiple antioxidant enzymes, as well as antioxidant vitamins and m
-
These experiments make it clear that one
2025-01-20
These experiments make it clear that one can study the effect of antimalaria drugs that target the DHFR enzyme of P. falciparum by transferring the malaria enzyme into S. cerevisiae. The ease of growth and manipulation of the yeast make it easy to measure the sensitivity of any particular dhfr allel
-
Although little is known about
2025-01-20
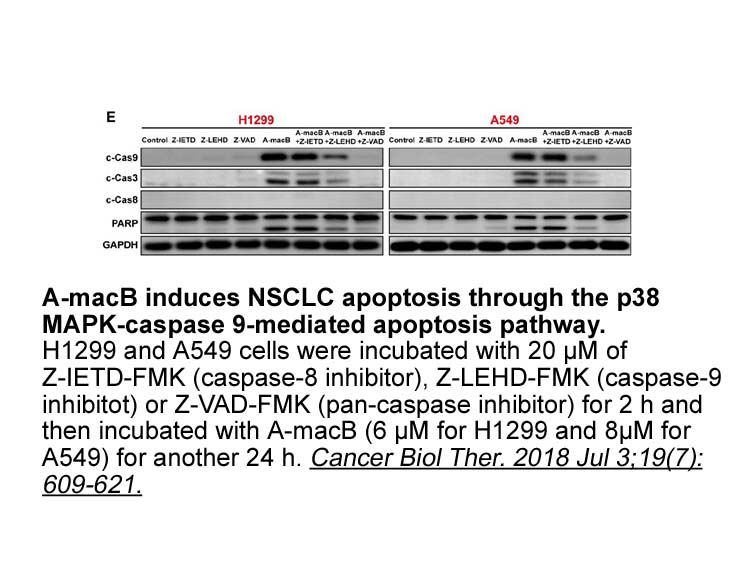
Although little is known about the etiopathogenesis of preeclampsia, this syndrome has a major impact on maternal and fetal health worldwide, since it is responsible for 10–15% of maternal deaths [16], [17], preterm births, intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), and fetal deaths [2]. In developing
-
br Androgen interference with the
2025-01-20
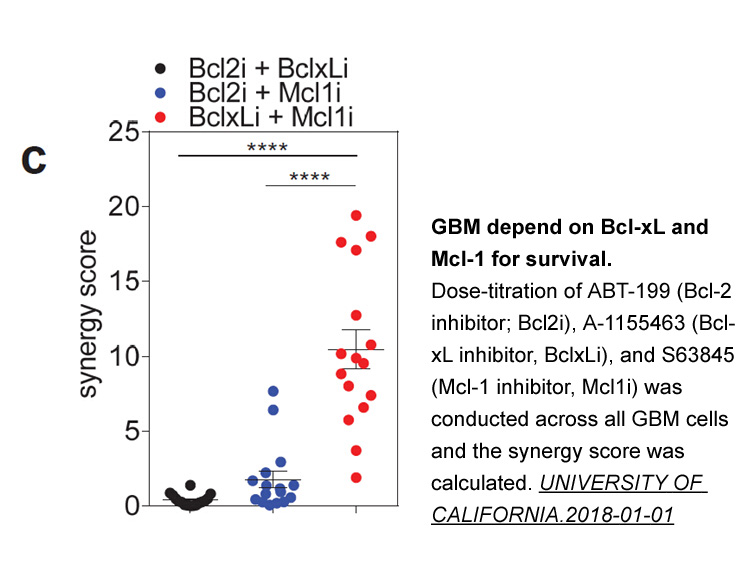
Androgen interference with the action of arachidonic AP1903 metabolites’ actions; the other side of the coin Arachidonic acid, being a polyunsaturated fatty acid present in the phospholipids of the membrane of cells, is highly abundant within the organism. It is mainly involved in cellular signa
-
Recent studies revealed that certain plant
2025-01-20
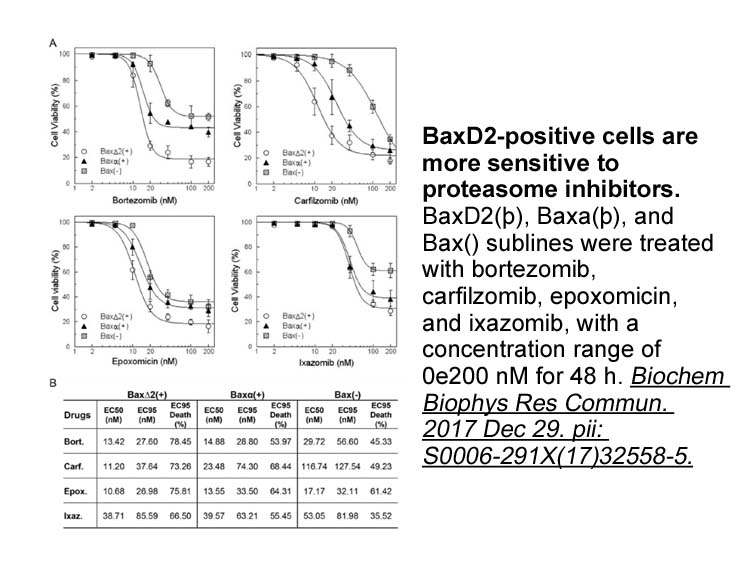
Recent studies revealed that certain plant-derived compounds can also interfere with AR function. One way of such an interference is by modulating its expression levels. This is the case for the two flavonoids quercetin and luteolin that have been reported to repress the function of AR by inhibiting
-
br Disclosure br Acknowledgments br Introduction Anaplastic
2025-01-20
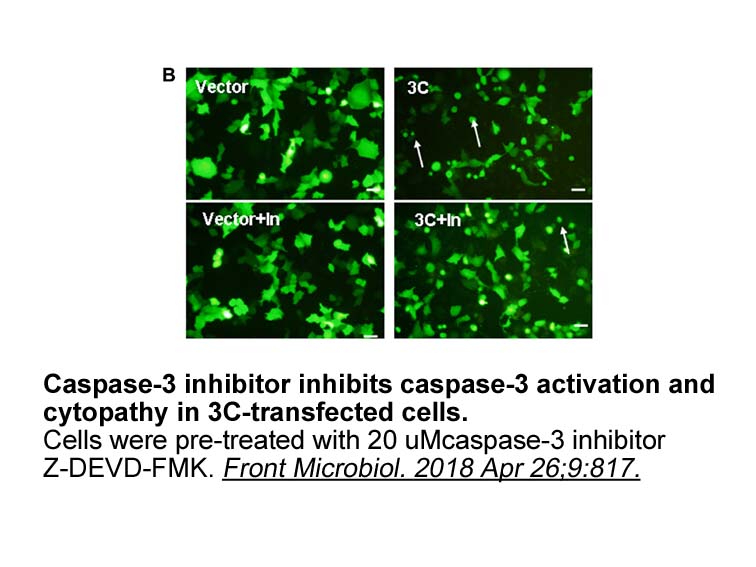
Disclosure Acknowledgments Introduction Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK), a receptor tyrosine kinase, belongs to the insulin receptor kinase subfamily [1]. Oncogenic activation of ALK is associated with the BLZ945 and progression of multiple human cancer types [2,3], including anaplastic l
-
Liao and van Linden et al divided the gap
2025-01-20
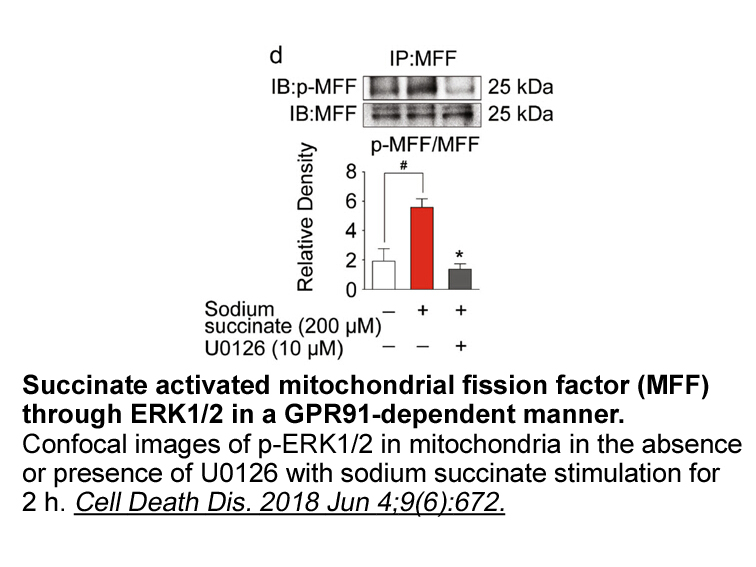
Liao [47] and van Linden et al. [48] divided the gap between the N-terminal and C-terminal lobes into a front cleft or pocket, a gate area, and a back cleft. The back pocket corresponds to the gate area and the back cleft. The front cleft includes the Gly-rich loop, the hinge, the linker connecting
-
In conclusion we show that HBP is
2025-01-20
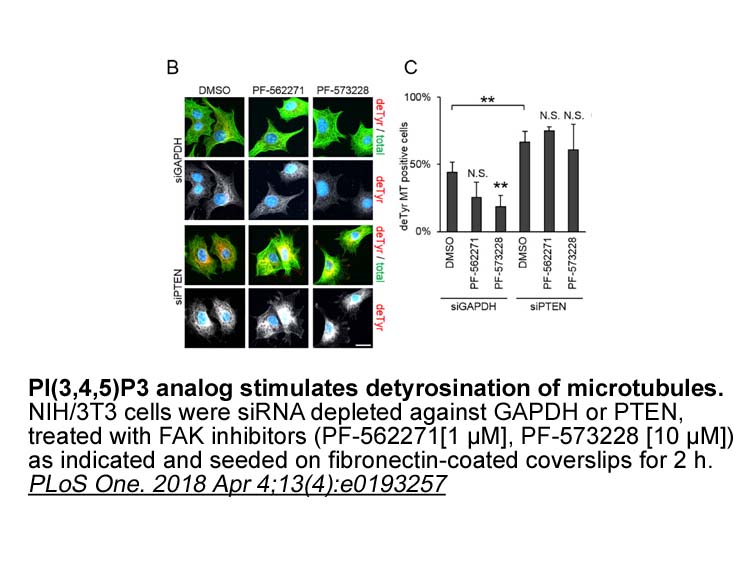
In conclusion, we show that HBP1 is phosphorylated on three sites, which control HBP1 transcriptional activity and glioblastoma cell proliferation. This phosphorylation largely depends on AKT, although other kinases may also be involved. In a previous study, we had shown that the PI3K-AKT pathway re
16277 records 33/1086 page Previous Next First page 上5页 3132333435 下5页 Last page